Python三维网格体素化
本文主要是实现将一个网格模型体素化,实现不同分辨率的体素化效果,并且可视化输出为obj文件!
首先利用trimesh对mesh进行采样,然后根据采样点得到各个体素点的占有值。
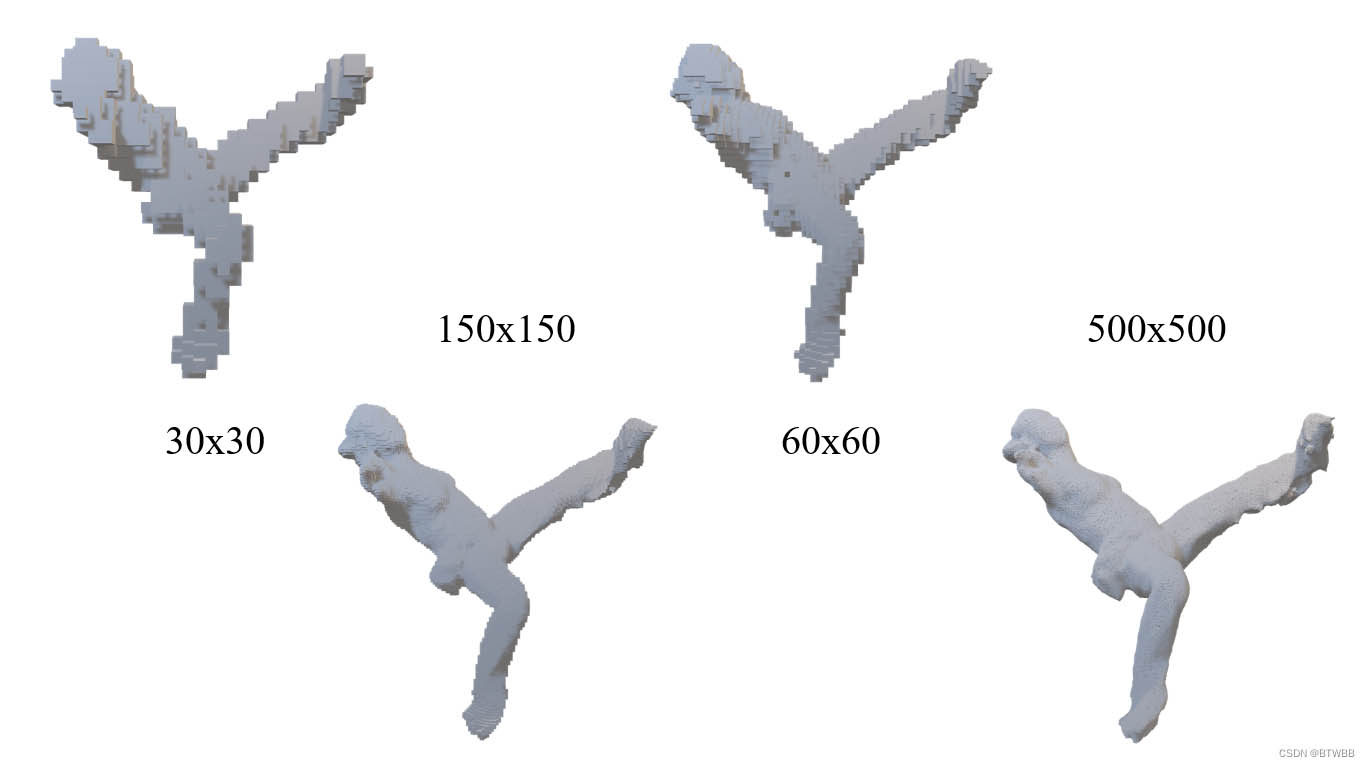
效果
通过调整分辨率以及采样率(当分辨率变高时建议适量提高采样率)得到以下的效果!

代码
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 |
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ @author: Matthieu Zins """
import trimesh import numpy as np import os import argparse
""" ====== Voxelize the surface of a mesh ====== """
def create_if_needed(folder): if not os.path.isdir(folder): os.mkdir(folder)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Pass object name') parser.add_argument('input_mesh', type=str) parser.add_argument('--output_folder', type=str, default="") parser.add_argument('--resolution', type=int, nargs=3, default=[50, 50, 50], help="resolution_X resolution_Y resolution_Z") parser.add_argument('--sampling', type=int, default="100000", help="number of points sampled on the mesh") args = parser.parse_args()
input_mesh_filename = args.input_mesh object_name = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(input_mesh_filename))[0] output_folder = args.output_folder if len(output_folder) == 0: output_folder = object_name RES_X, RES_Y, RES_Z = args.resolution sample_points_count = args.sampling
create_if_needed(output_folder)
mesh = trimesh.exchange.load.load(input_mesh_filename)
# Uniform Points Sampling pts, _ = trimesh.sample.sample_surface_even(mesh, sample_points_count )
# Save sample points sampled_points_mesh = trimesh.Trimesh(vertices=pts) sampled_points_mesh.export(os.path.join(output_folder, object_name + "_resampled_points.ply"))
# Adjust the grid origin and voxels size origin = pts.min(axis=0) dimensions = pts.max(axis=0) - pts.min(axis=0) scales = np.divide(dimensions, np.array([RES_X-1, RES_Y-1, RES_Z-1])) scale = np.max(scales)
# Voxelize
pts -= origin pts /= scale pts_int = np.round(pts).astype(int)
grid = np.zeros((RES_X, RES_Y, RES_Z), dtype=int) gooRES_X = np.where(np.logical_and(pts_int[:, 0] >= 0, pts_int[:, 0] < RES_X))[0] gooRES_Y = np.where(np.logical_and(pts_int[:, 1] >= 0, pts_int[:, 1] < RES_Y))[0] gooRES_Z = np.where(np.logical_and(pts_int[:, 2] >= 0, pts_int[:, 2] < RES_Z))[0] goods = np.intersect1d(np.intersect1d(gooRES_X, gooRES_Y), gooRES_Z) pts_int = pts_int[goods, :] grid[pts_int[:, 0], pts_int[:, 1], pts_int[:, 2]] = 1
# Save voxels voxel_pts = np.array([[-0.5, 0.5, -0.5], [0.5, 0.5, -0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [-0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [-0.5, -0.5, -0.5], [0.5, -0.5, -0.5], [0.5, -0.5, 0.5], [-0.5, -0.5, 0.5]]) voxel_faces = np.array([[0, 1, 2, 3], [1, 5, 6, 2], [5, 4, 7, 6], [4, 0, 3, 7], [0, 4, 5, 1], [7, 3, 2, 6]])
def get_voxel(i, j, k): global voxel_pts, voxel_faces v = np.array([i, j, k], dtype=float) * scale v += origin points = voxel_pts * scale + v return points, voxel_faces.copy()
points = [] faces = [] fi = 0 for i in range(RES_X): for j in range(RES_Y): for k in range(RES_Z): if grid[i, j, k]: p, f = get_voxel(i, j, k) points.append(p) f += fi faces.append(f) fi += 8
points = np.vstack(points) faces = np.vstack(faces) # Write obj mesh with quad faces with open(os.path.join(output_folder, object_name + "_voxels.obj"), "w") as fout: for p in points:fout.write("v " + " ".join(map(str, p)) + "\n") for f in faces+1:fout.write("f " + " ".join(map(str, f)) + "\n")
print(object_name, "done.") |
运行:
Dependencies
-
numpy
-
trimesh
|
1 2 3 |
## Usage
python voxelize_surface.py example/chair.obj --output_folder output --resolution 30 30 30 --sampling 10000 |
The optional parameters are:
-
output_folder (string): folder where the result is saved
-
resolution (list): the resolution of the grid [res_x, res_y, res_z]
-
sampling (int): number of points sampled on the mesh surface before voxelization
-
注:输入的类型可以时obj也可以是off以及ply格式!
注意:
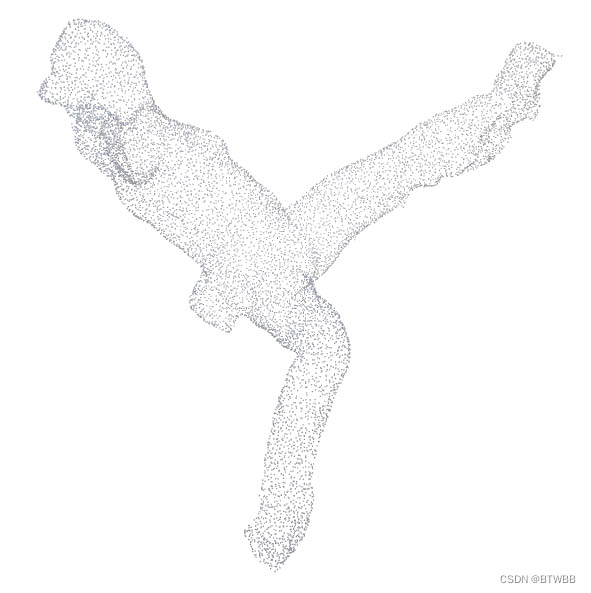
若出现如下情况,可将采样点数(sampling)提高!
出现此种情况的原因是采样间隔太大,而体素尺寸太小(分辨太高),所以导致在有些体素的占有值进行判断的时候出现错误。
所以也可以通过降低分辨率来改善此种情况!

Reference:
声明:本文的代码并非原创,来自GitHub中zinsmatt的Surface_Voxels一作!若有侵权请联系撤文!
https://github.com/zinsmatt/Surface_Voxels











 浙公网安备
33010802011855号
浙公网安备
33010802011855号